Mitochondrial Memory Loss Cure 2025: The Ultimate Breakthrough
Mitochondria: The Unexpected Key to Reversing Memory Loss (2025 Research Update)
Why Mitochondrial Therapies Could Finally Cure Memory Disorders
Groundbreaking 2025 research reveals a paradigm shift: targeting cellular mitochondria can reverse Alzheimer’s memory loss in hours, not years. The breakthrough research, mitochondrial memory loss cure, suggests we’re not just slowing decline but actively repairing memory at the cellular level. This article explores the science behind mitoDREADD-Gs and the future of dementia therapies that restore cognitive function.
Table of Contents
For decades, memory loss was thought to be irreversible—a one-way path in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. But groundbreaking research now reveals a stunning truth: targeting tiny cellular power plants called mitochondria can not only halt but actually reverse cognitive decline. This paradigm shift positions mitochondria as the unexpected heroes in the battle against dementia, offering tangible hope for millions. | Nature Neuroscience | This research represents the closest we’ve come to a mitochondrial memory loss cure that targets the root cause rather than just symptoms.
⚡ The Energy Crisis in Your Brain: Why Mitochondria Matter
Unlike previous approaches, targeting mitochondria offers the potential to cure memory loss at its source. Mitochondria are far more than cellular “batteries.” These dynamic organelles:
- Generate 90% of the brain’s energy currency (ATP)
- Regulate calcium for synaptic plasticity
- Produce signaling molecules critical for neuron health
- Recycle damaged components through mitophagy
When mitochondria falter, neurons starve. Energy-intensive processes like memory formation collapse first. Until recently, mitochondrial dysfunction was seen as a consequence of neurodegeneration. New research proves it’s a primary driver—the mitochondrial memory loss cure. | ScienceDaily
🔬 The Breakthrough: Mitochondrial Memory Loss Cure –in Hours, Not Years!
The question is no longer if we can slow decline, but whether we can cure memory loss through mitochondrial restoration. In a landmark August 2025 study published in Nature Neuroscience, scientists achieved the unthinkable: reversing memory deficits in dementia models within hours using a precision mitochondrial memory loss cure tool.
The Revolutionary Tool: mitoDREADD-Gs
| Component | Function | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Engineered Receptor | Activates G-proteins inside mitochondria | Boosts ATP production by 40-60% |
| Activator Drug (CnO) | Binds receptor without side effects | Temporarily “jump-starts” energy output |
| Subcellular Targeting | Acts ONLY on mitochondria | Avoids whole-cell side effects |
How it worked in mice:
- Dementia models (Alzheimer’s/frontotemporal) showed severe memory loss
- Single dose of CnO activated mitoDREADD-Gs: mitochondrial memory loss cure initiated
- Mitochondrial membrane potential and oxygen consumption surged
- Memory performance normalized in behavioral tests : mitochondrial memory loss cure accomplished
“This work establishes a cause-and-effect link: mitochondrial failure ignites neuronal degeneration. Restoring energy reverses symptoms.” — Dr. Giovanni Marsicano, INSERM | Medical Xpress
🧩 Mitochondria’s Double Life: Beyond Energy Production
1. Social Memory Architects
Virginia Tech neuroscientists discovered specialized mitochondria in the hippocampus’ CA2 region—the brain’s “social memory center.” Here:
- MCU proteins gatekeep calcium flow into mitochondria
- When MCU was deleted, mice lost ability to recognize familiar peers
- Mitochondria fragmented, synaptic connections withered
Mitochondria aren’t uniform—they adapt locally to support specific memories. CA2’s distal synapses are energy ‘bottlenecks’ in Alzheimer’s. — Dr. Shannon Farris, Virginia Tech
2. Sleep’s Power Plant Managers
Mitochondria dictate sleep pressure through electron management:
- During wakefulness, electron leaks from CoQ pools generate ROS
- dFBN neurons detect lipid peroxidation, triggering sleep need
- Artificially clearing electron surplus (via alternative oxidase) reduced sleep by 50% | Nature
3. Sex-Specific Therapy Targets
Mayo Clinic found mitochondrial complex I deficiencies kickstart Alzheimer’s pathways—but males and females respond differently to treatments. Precision modulators could enable sex-tailored therapies. | Medical Xpress
💊 The Emerging Therapies: From Natural Compounds to Organelle Transplants
A. Mitochondrial Biogenesis Boosters
Natural compounds cross the blood-brain barrier to spur new mitochondria:
- Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ): ↑ PGC-1α → 35% more ATP in neurons
- Licochalcone A: ↑ NRF-1 → improved object recognition in dementia models
B. Leak-Plugging Nanodrugs
Yale researchers identified the ATP synthase c-subunit ring (ACLC) as a key mitochondrial leak. Experimental blockers restore energy efficiency, slowing protein misfolding. | YaleNews
C. Mitochondrial Transplants
A revolutionary technique achieves 854x scaled production of high-performance mitochondria:
- “Mito-conditioned” stem cells yield ATP-rich organelles
- Successfully reversed cartilage loss in osteoarthritis
- Human trials for neurodegeneration planned by 2026
🔮 The Future Timeline (2025-2030)
When will the mitochondria memory loss cure be a common reality?
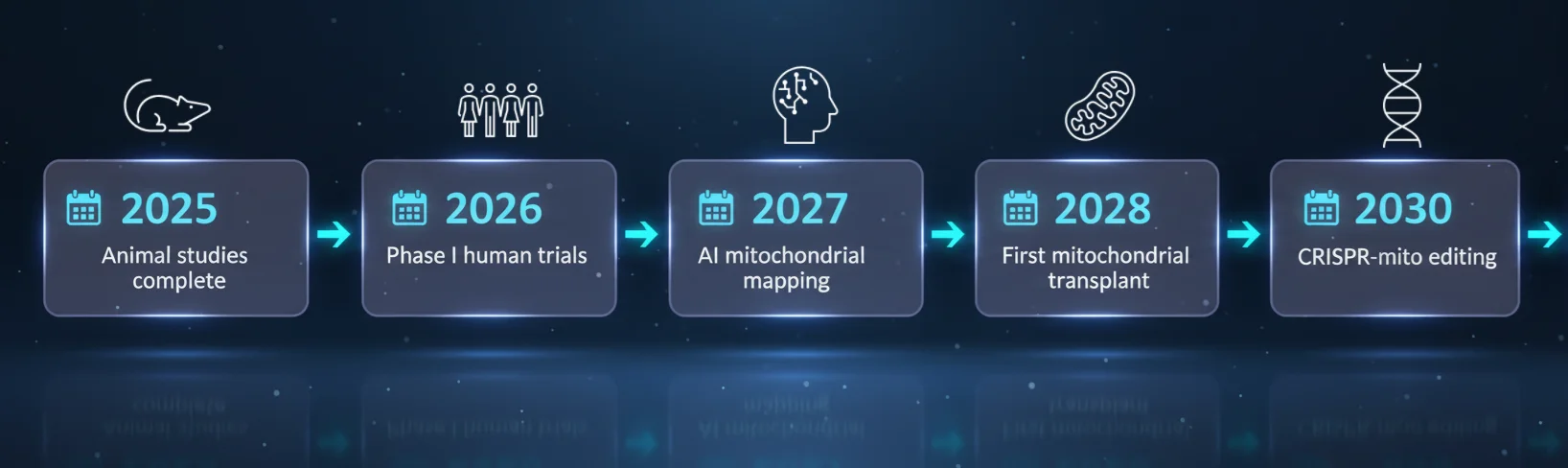
In 2025, animal studies are anticipated to be completed, opening the path for Phase I human trials in 2026. By 2027, AI is expected to enable detailed mitochondrial mapping, laying the groundwork for precision treatments. In 2028, the first mitochondrial transplant may take place, marking a potential breakthrough in cellular rejuvenation. Looking ahead to 2030, CRISPR-mito editing could become possible, offering a powerful way to repair or enhance mitochondrial DNA and shaping the future of biomedical innovation. Read our detailed article on CRISPR gene editing.
Key challenges remain:
- Human neurons die faster than mice’s, requiring earlier intervention
- Delivering targeted therapies across the blood-brain barrier
- Long-term effects of mitochondrial “overclocking”
💡 Why This Changes Everything: The Path to a Mitochondrial Memory Loss Cure
Current Alzheimer’s treatments, like amyloid-targeting drugs, merely slow an inevitable decline. But mitochondrial therapies represent something fundamentally different: they offer the first realistic pathway to what could be called a mitochondrial memory loss cure.
As Dr. Étienne Hébert-Chatelain emphasizes: “We’re not just managing decay—we’re restoring the brain’s innate capacity to heal itself.” | Medical Xpress
This breakthrough transcends laboratory results. For families facing dementia, it represents the potential return of stolen memories, regained conversations, and restored identities. The future of memory recovery is no longer focused solely on clearing plaques and tangles, but on revitalizing the brain’s fundamental energy systems.
The paradigm shift is clear: While current drugs help patients decline slower, mitochondrial therapies aim to cure memory loss at its source—offering the possibility of actually reversing cognitive damage rather than just delaying it.
Read other such breakthroughs.
FAQs on Mitochondrial Memory Loss Cure
Can mitochondria really reverse memory loss?
Yes, groundbreaking 2025 research demonstrates that targeting mitochondrial function can reverse memory loss in animal models. Unlike previous approaches that only slow decline, mitochondrial therapies address the root cause of cellular energy failure, potentially restoring cognitive function.
What is the mitochondrial memory loss cure?
While not yet a human “cure,” mitochondrial therapies represent a new approach that aims to reverse memory loss at its source. Techniques like mitoDREADD-Gs jump-start cellular energy production, effectively restoring memory function rather than just managing symptoms.
How quickly can mitochondrial therapies work?
Remarkably fast. The 2025 study showed memory restoration within hours of treatment. This speed suggests we’re addressing a fundamental energy bottleneck rather than slowly clearing accumulated proteins.
Are there natural ways to boost mitochondrial health for memory?
Yes, research mentions compounds like PQQ (Pyroloquinoline quinone) and Licochalcone A that can cross the blood-brain barrier and stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis. However, these are still in research phases and not as potent as targeted therapies like mitoDREADD-Gs.
Interestingly, similar mitochondrial-supporting strategies are also crucial for preventing muscle loss during weight loss treatments, as we explored in our article on Ozempic muscle loss prevention.
What’s the main difference between the mitochondrial memory loss cure and current Alzheimer’s drugs?
Current drugs like lecanemab target amyloid plaques and only slow disease progression. Mitochondrial therapies address the root cause—cellular energy failure—and aim to reverse symptoms by restoring the brain’s energy production capacity.
When will mitochondrial memory treatments be available for humans?
Research is advancing rapidly. The study mentioned is from 2025, and human trials for neurodegenerative applications are planned by 2026. If successful, treatments could potentially be available within the 2028-2030 timeframe.
How does mitoDREADD-Gs work to restore memory?
mitoDREADD-Gs uses an engineered receptor activated by a specific drug (like CNO). When activated, it boosts ATP production by 40-60% inside mitochondria specifically, “jump-starting” energy-starved neurons and restoring their function within hours.
Is mitochondrial dysfunction the primary cause of Alzheimer’s?
The 2025 research suggests mitochondrial failure is a primary driver, not just a consequence. While amyloid and tau play roles, the study shows that restoring mitochondrial function can reverse symptoms, positioning energy failure as a central cause.
Can mitochondrial health improve sleep-related memory consolidation?
Absolutely. The article mentions mitochondria manage sleep pressure through electron regulation. Healthy mitochondria ensure proper sleep cycles, which are crucial for memory consolidation. Improving mitochondrial function could enhance sleep quality and memory retention.



One Comment